What Toxic Substance is Released When Welding Stainless Steel
The Toxic Substance Released During Stainless Steel Welding
Welding is a common and essential process in many industries, particularly in the fabrication and repair of stainless steel products. However, this process is not without its hazards. One of the significant concerns in welding stainless steel is the release of a toxic substance that poses health risks to welders. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore what this substance is, the dangers it presents, and how to mitigate these risks effectively.
Understanding the Hazard: Chromium VI
What Is Chromium VI?
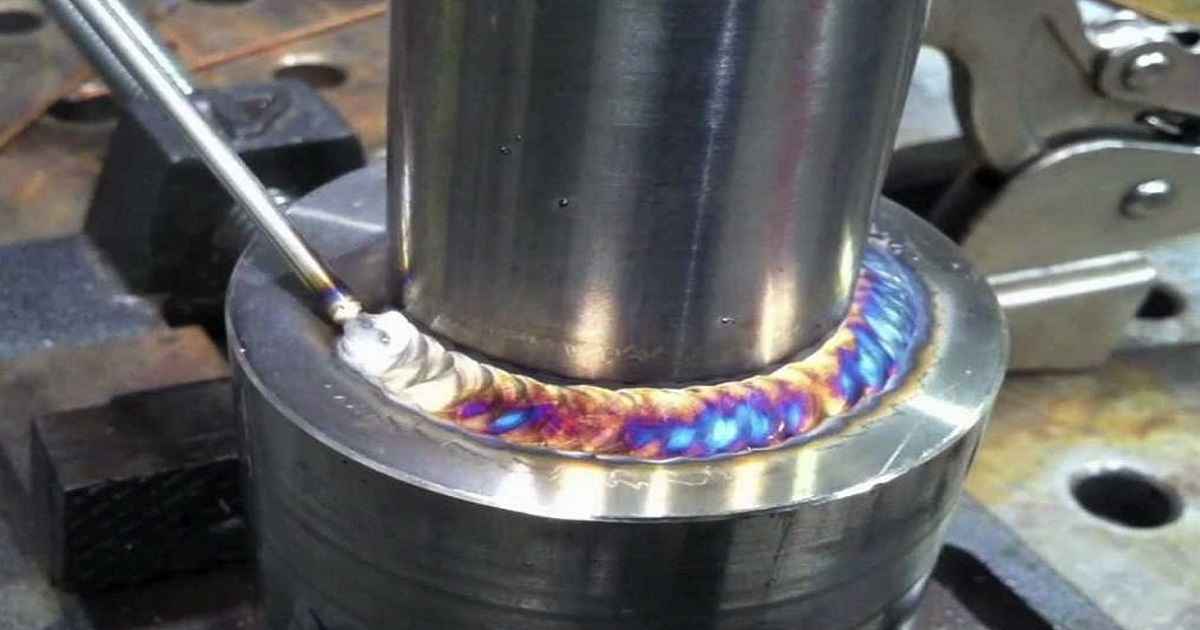
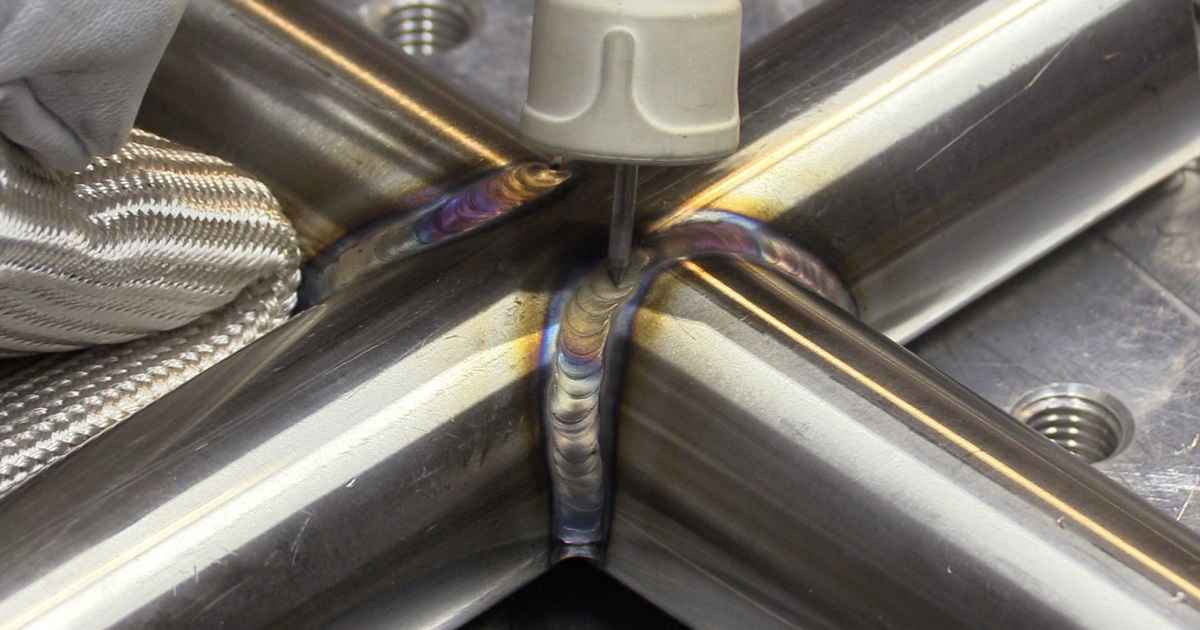
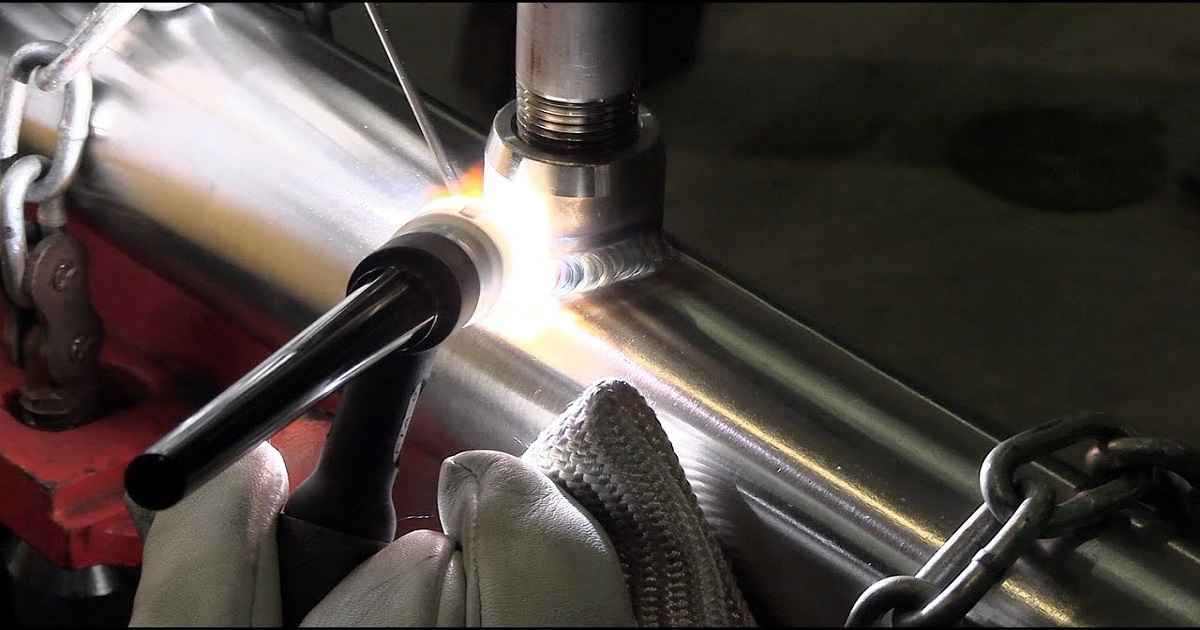
The toxic substance released during the welding of stainless steel is Chromium VI, also known as hexavalent chromium. Stainless steel contains chromium, which, when heated to high temperatures during welding, can oxidize and form Chromium VI.
How Is Chromium VI Produced in Welding?
When stainless steel is welded, the intense heat from the welding arc can cause chemical reactions in the metal. Chromium, a component of stainless steel, reacts with oxygen in the air to form Chromium VI, which is then released as part of the welding fumes.
Health Risks Associated with Chromium VI
Acute Exposure Risks
Short-term exposure to Chromium VI can cause irritation of the eyes, skin, and respiratory system. Symptoms may include redness and itching of the skin, a burning sensation in the nose and throat, and coughing.
Long-Term Exposure Risks
Chronic exposure to Chromium VI poses more severe health risks. It is a known carcinogen, linked to an increased risk of lung cancer. Prolonged exposure can also lead to damage to the respiratory system, skin conditions, and potential impacts on the liver and kidneys.
Safety Measures and Best Practices
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Wearing appropriate PPE is crucial when welding stainless steel. This includes a welding helmet with proper filtration to protect from fumes, respirators, gloves, and protective clothing to prevent skin exposure.
Ventilation and Extraction Systems
Proper ventilation is essential to disperse toxic fumes. Use of local exhaust ventilation systems at the welding site can significantly reduce the concentration of Chromium VI in the air.
Training and Awareness
Welders should be adequately trained about the risks associated with Chromium VI and the correct use of safety equipment and procedures. Regular safety training and awareness programs can help maintain a safe working environment.
Regulatory Guidelines and Compliance
Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) Standards
OSHA has set specific standards for exposure to Chromium VI in the workplace. These regulations outline permissible exposure limits and requirements for protective measures, monitoring, and medical surveillance.
Compliance and Monitoring
Employers are responsible for ensuring compliance with safety standards. This includes regular monitoring of Chromium VI levels in the workplace and providing medical examinations for workers exposed to high levels.
Advanced Welding Techniques to Reduce Exposure
Alternative Welding Methods
Certain welding methods produce less Chromium VI. Exploring alternative techniques that generate lower fume levels can be beneficial.
Use of Low-Chromium Electrodes
Using welding electrodes that contain lower levels of chromium can reduce the amount of Chromium VI produced during welding.
FAQs: Addressing Your Concerns
What immediate steps should be taken if exposed to Chromium VI?
If you suspect exposure to Chromium VI, it’s important to leave the contaminated area immediately, seek fresh air, and remove any contaminated clothing. Seek medical attention for any symptoms or concerns.
Can Chromium VI be completely eliminated from welding fumes?
While it’s challenging to eliminate Chromium VI entirely from welding fumes, its concentration can be significantly reduced through proper techniques, equipment, and safety measures.
By recognizing the dangers posed by Chromium VI and adopting effective safety protocols, the welding industry can continue its essential work while safeguarding the health of its workers.
Conclusion: Prioritizing Safety in Stainless Steel Welding
Welding stainless steel is a necessary process in many manufacturing and construction activities, but it must be approached with an awareness of the potential hazards. Understanding the risks associated with Chromium VI and implementing stringent safety measures and best practices are essential to protect the health and well-being of welders. By staying informed and vigilant, we can ensure that the benefits of welding stainless steel are not overshadowed by the risks.